What is the age of the rocks on the surface of the footwall side of the fault relative to those on the hanging wall.
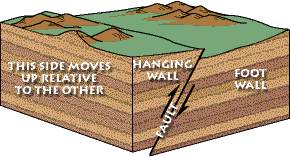
In a fault the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall.
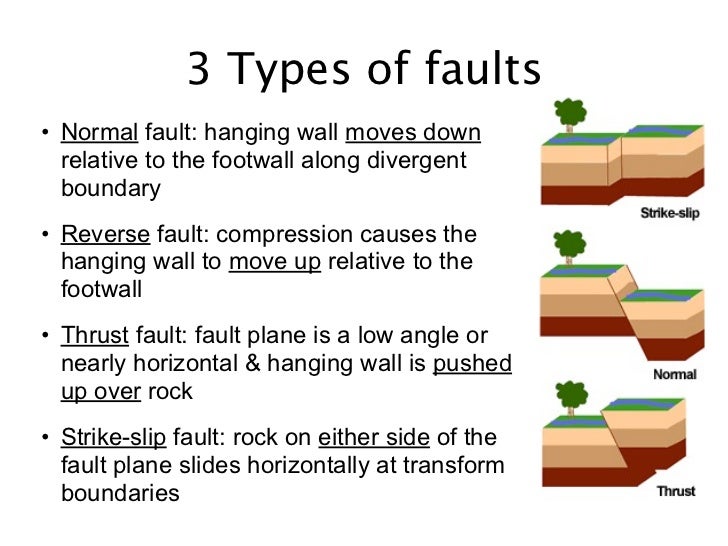
In thrust or reverse faults the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall and in strike slip faults it moves horizontally relative to the footwall.
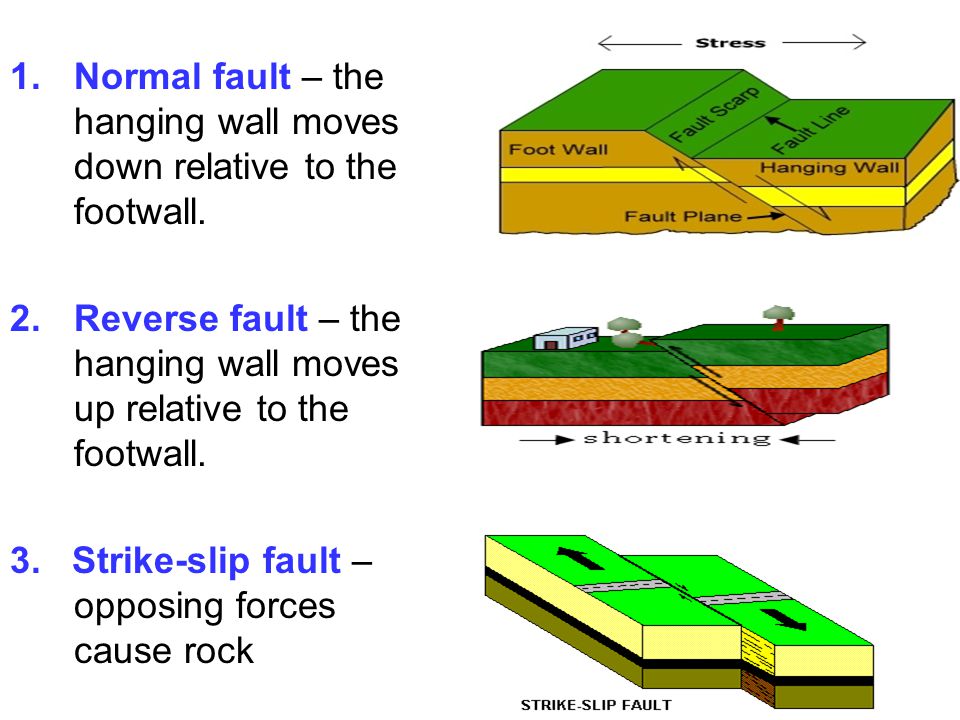
This is true of normal faults.
This is true of normal faults.
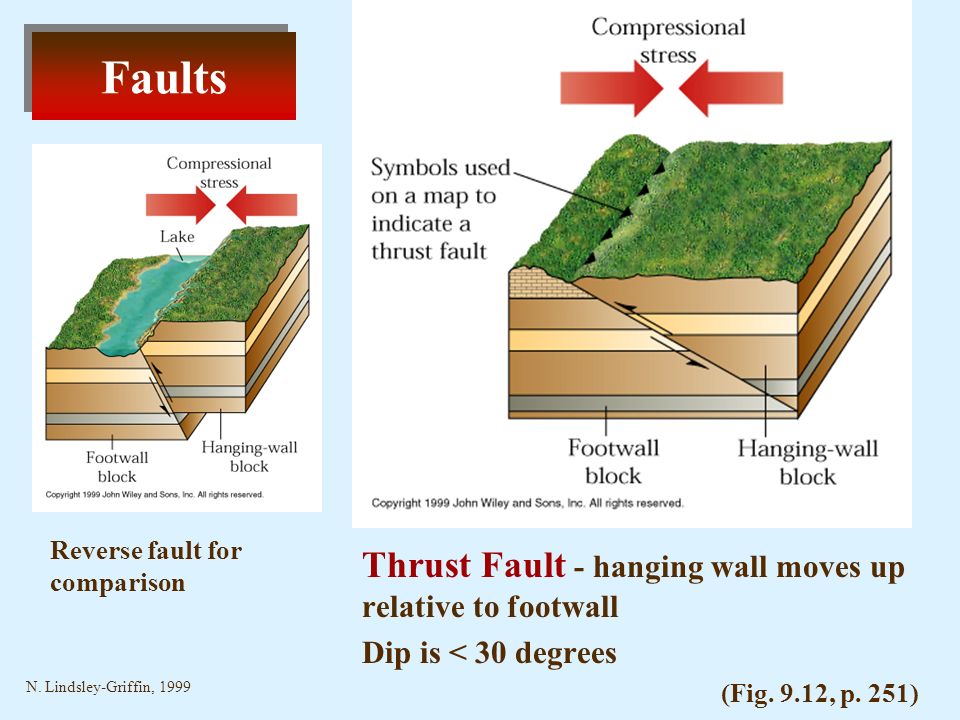
Reverse faults indicate compressive shortening of the crust.
When the hanging wall moves up in relative to the footwall it is called a fault.
Strike slip faults are right lateral or left lateral depending on whether the block on the opposite side of the fault from an observer has moved to the right or left.
In thrust or reverse faults the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall and in strike slip faults it moves horizontally relative to the footwall.
The dip of a reverse fault is relatively steep greater than 45.
In dip slip faults if the hanging wall block moves downward relative to the footwall read more.
To the dip is called dip slip faulting.
The terminology of normal and reverse comes from coal mining in england where normal faults are the most common.
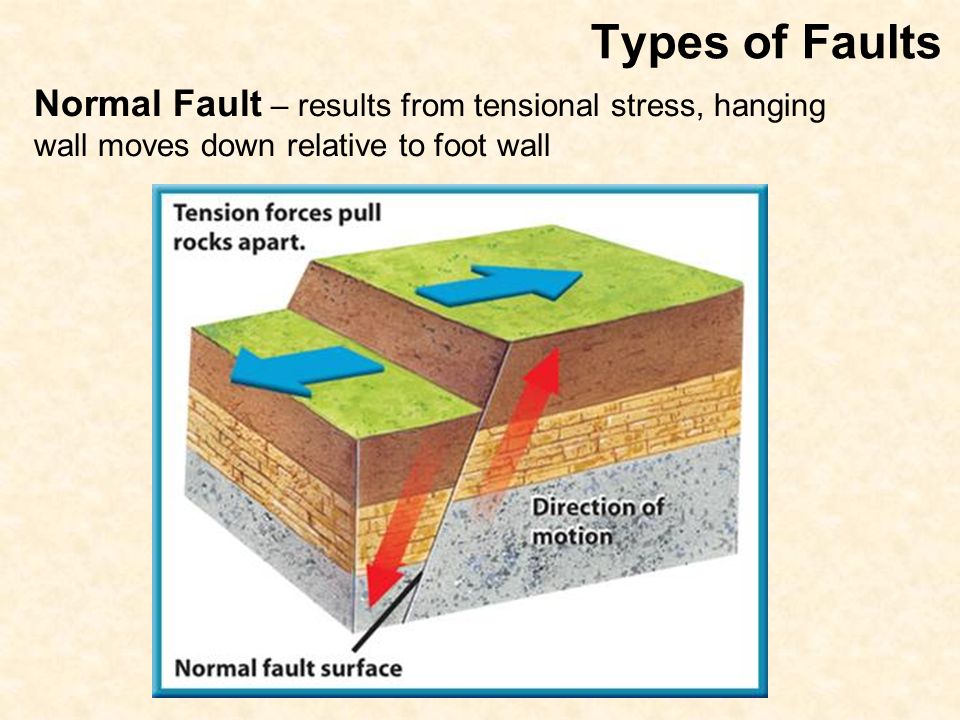
These usually occur when tectonic forces cause tension that pulls rocks apart.
After the occurrence of a normal dip slip fault in flat lying sedimentary rocks the fault scarp produced is eliminated by erosion.
Describe three types of faults.
When the hanging wall moves down in relative to the footwall it is called a fault.